by Natalie Suzelis
In The Green New Deal and Beyond: Ending the Climate Emergency While We Still Can, Stan Cox has a message for all who were counting on the Green New Deal to help save us from ecological and economic collapse: this legislation will not go far enough. Cox’s book comes at a sobering time, when the only two U.S. presidential candidates he mentions as being in favor of the Green New Deal—Bernie Sanders and Elizabeth Warren—have fallen behind a ‘more electable’ candidate who has not expressed such enthusiastic support for GND policies. In light of such developments, and in light of the global health crisis now facing the world, a manuscript devoted to many of the GND’s shortcomings might seem untimely. Yet Cox provides important insights into how our intersecting crises—ecological, economic, and epidemiological—could lead to a positive restructuring of the economy, if we can push such legislation to meet them. To do so, Cox argues, requires expanding the GND’s restorative approach to environmental justice, a willingness to reinvent the economy at a scale not seen since World War II, and the prioritizing of people and the planet above economic growth.
There are a few assumptions of the Green New Deal with which Cox takes issue, given how far we have advanced on the climate clock. These include the legislation’s vision to build up ‘green’ energy capacity and its promise to maintain and even accelerate economic growth. First, Cox addresses the common assumption that clean energy will push out old, dirty energy, by showing that there is so far no evidence to support that this will happen. As Cox shows from previous cap-and-trade policies, new energy sources are more likely to add to the existing energy supply than replace it. So far, the attempt to phase out fossil fuel energy with solar and wind power has only served to supplement the energy market and, sometimes, even enhance the production and trade of fossil fuels. Therefore, the parts of the GND which promise to re-grow the economy by replacing fossil fuels with renewable or clean energy sources are simply not realistic. To reach the goal of clean energy by 2030 through solar and wind power, we would have to build infrastructure for such industries ‘at thirty-three times the highest rate of buildup ever achieved to date’ and at scale which would infringe upon land and water which we would do better to conserve.
Cox urges us to accept that while we must phase out fossil fuels now with a strong cap on fossil fuel production, we must also accept that such a rapid phasing out of fossil fuels will shrink GDP.
Instead, Cox urges us to accept that while we must phase out fossil fuels now with a strong cap on fossil fuel production, we must also accept that such a rapid phasing out of fossil fuels will shrink GDP. This insight brings some of the Green New Deal’s aims in conflict with one another. In the legislation’s own language, the GND proposes to bring ‘unprecedented levels of prosperity’ and a new era of ‘domestic manufacturing in the United States,’ while also ‘restoring and protecting threatened, endangered, and fragile ecosystems.’ Yet as Cox points out, land and soil restoration alone will take a massive amount of work and coordination. The GND would then have to choose between such restoration and the massive building of new industries. Cox argues that the choice should be clear for those who truly know what is at stake. Because the GND also aims to ‘promote justice and equity by stopping current, preventing future, and repairing historic oppression of indigenous communities, communities of color, migrant communities, deindustrialized communities, depopulated rural communities, the poor, low-income workers, women, the elderly, the unhoused, people with disabilities, and youth’ Cox argues that it cannot do so while also drastically reducing emissions and growing a new energy market.
What’s new is also old
To help us understand how we might avoid some of these assumptions, Cox points to a few lessons learned from the old New Deal. What is not new about the Green New Deal, for example, is its ambitious goal to take on the task of essentially planning the entire economy as a necessary response to economic and ecological crisis. Although it may seem unthinkable after decades of neoliberalism, structural adjustment, and austerity, Cox reminds us that Roosevelt himself had introduced the New Deal by publicly acknowledging that ‘free market policies and resource extraction’ had created a fiscal and ecological emergency that required an entirely new — and entirely planned—economy (3). The government’s ability to take the reins from the free market was the first step in the New Deal’s success. The second, and more essential step, was that a national labor movement held this project accountable to workers. This labor pressure, which resulted in the passing of the National Labor Relations Act, helped ensure that the projects and stimulus packages meant to plan both production and consumption specifically addressed the rights struggles of working people along with the conservation and maintenance of the environment.
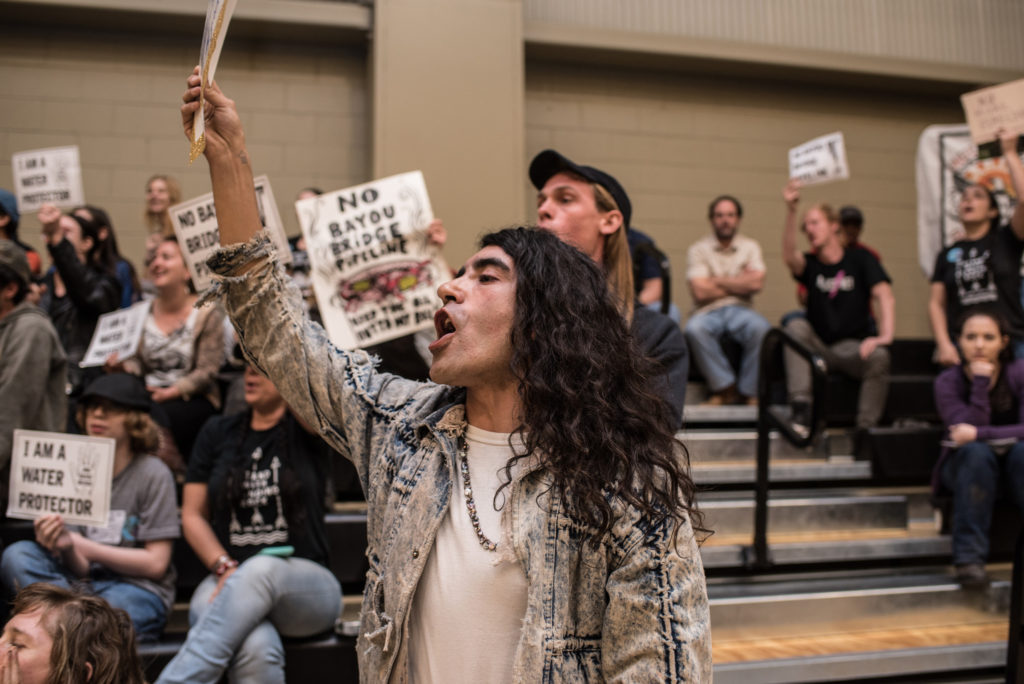
Yet what made the New Deal unsuccessful was its failure to implement its goals across racial lines. As Cox acknowledges, rather than helping Black workers in the South, for example, the New Deal cemented institutional racism by deferring to locally prevailing wages for occupations dominated by Black workers. Further, the Social Security Act of 1935 did not cover farm laborers nor domestic workers, which employed two-thirds of the Black population, and the New Deal’s housing policies perpetuated residential segregation. In order to learn from this history, Cox points us to the successful campaign of the Southern Tenant Farmers Union, which recruited thousands to stage a successful strike that demanded higher wages for Black and white farmworkers across northeast Arkansas. The goal of this organization was both a protest movement and a labor union: agitation and publicity, along with strikes and collective bargaining, aimed to put pressure on the New Deal and present radical alternatives to its policy. Similarly, no matter how progressive the Green New Deal’s goals, Cox argues that it must also face relentless pressure from unions, social movements, activists, and groups like Indigenous Climate Action, Sunrise Movement, Keep it in the Ground, and Fridays For Future, in solidarity with land and water protectors who are already struggling to defend some of the world’s largest carbon sinks.
The GND does take some of the New Deal’s key mistakes into account, in arguing for the importance of protecting First Nations and marginalized communities. Yet more pressure will be required to recognize the hard truth that we have already overshot our shared limit of fossil fuel production and consumption, and that even the clean energy of new public infrastructure would rely upon dangerous extractive practices that threaten marginalized communities and the sovereignty of indigenous lands. Climate activists, scholars, and the public must therefore ask themselves: can the GND really ensure a just energy transition by building a roaring new ‘green’ economy and mining raw materials like cobalt, cooper, lithium from around the world, which, as Cox points out, are both notoriously associated with human rights abuses and harmful extraction (68)? What the optimism of the GND does not appear to be taking into account is that the mining of such materials—even those meant to produce ‘clean’ or ‘renewable’ energy—is going to remain a dirty business.
We must be willing to cut the wasteful parts of this economy in the same way that the War Productions Board of the 1940s cut, simplified, and restructured the U.S. economy of the 1940s.
Further, what the GND seems to have not learned from the history of the New Deal is that a stimulus package by itself will not go far enough. In the case of the New Deal, as Cox points out, it was ultimately not the massive stimulus but the United States’ transition into a war economy that addressed both unemployment and overproduction. This is also why the United States, to this day, relies upon its military to help expand a GDP that is fundamentally linked to high carbon emissions. While the fact that the U.S. military is a bigger polluter than most countries is well known, what is less known, as Cox asserts, is that we must be willing to cut the wasteful parts of this economy in the same way that the War Productions Board of the 1940s cut, simplified, and restructured the U.S. economy of the 1940s.
A rationing economy
In what has become a rather prescient observation, given the current state of emergency brought on by the spread of COVID-19, Cox reminds us that it was not the New Deal, but the ‘emergency’ of World War II which allowed the U.S. to entirely restructure its system of production and consumption. In 1936, when the Roosevelt administration began easing off stimulus support, unemployment leapt back up to 19% and remained above fourteen percent until the war effort redirected its production to war-related materials and projects. Having spent $62 billion on stimulating the economy over the last eight years, Congress then spent $321 billion over the next five years in its transitioning to a war economy. Cox points out that while this new form of spending worked in restructuring production and consumption, many forget the sacrifices that were made to ensure a successful transition. A key element often left out, for example, is the War Production Board’s mandatory clampdown on prices as well as its rationing efforts, which aimed to ensure adequate food, shelter, clothing, and other basic necessities for the entire population. To this end, the War Production Board shrank, standardized, and simplified the economy in order to reduce civilian rail travel, prohibit the shipping of retail packages, and reduce the number and varieties of most commercial products.
Here Cox lingers on the point of the War Production Board’s tight rationing of goods, which included both food and fossil fuels. This is because, for Cox, proper rationing will be fundamental to a just energy transition. In making connections between the WPB’s tight regulation of the economy and what he argues should be a similar response to the emergency of ecological collapse, Cox chronicles how households were issued a monthly set of stamps for meats, cheeses, butter, sugar, fuel oil, kerosene, gasoline, tires, cars, bicycles, stoves, typewriters, shoes, coffee, canned fish and milk, fats, and other processed goods. Drivers began carpooling to work and families across the country planted 22 million ‘victory gardens’ to supplement the rationing system. Rather than being a hardship, Cox argues, rationing improved nutrition across economic classes and was met with overwhelming public approval. Even when ‘rationing was at its zenith,’ as Cox reports, approval outweighed disapproval by two to one, because civilians believed rationing was necessary to eliminate food shortages and conserve important raw materials. Cox insists that the same mindset must accompany the Green New Deal, which would entail a concerted effort on the part of national, state, and local legislation to ration electricity with the same zeal that this country has historically reserved for wartime.
Rations but not population control
Rationing off of overblown production and consumption of fossil fuels will not be as difficult for some as for others. Eighty percent of the population, as Cox reminds us, does not fly. Yet for all of Cox’s attention to detail in how to redistribute equitable energy consumption, there is one part of his enthusiasm for rationing that might give us pause, however. At one point, Cox suggests that one possible rationing formula might be ‘equal numbers of credits per adult for each energy source, with an additional half-credit for up to two children per household’ (103). Readers who have been following eagerly along may experience some dismay here. Why only up to two children, why only a half-credit per child, and what about children with special needs, for example, who might require a certain amount of technology? At this point in the book, it would have been helpful for Cox to engage with critiques of Malthusian population control, which is a well-known slippery slope in seeing the violence of climate catastrophe—and even epidemics—as helping to lower carbon footprint by lowering population. Recent takes about the spread of COVID-19 being a kind of ‘vaccine’ for humanity, for example, operate in precisely this Malthusian vein. Such presumptions forget that it is the safest and wealthiest classes who are responsible for the most emissions and even the spread of global disease, and that those least responsible for ecological and epidemiological crises are most vulnerable in their lack of access to healthcare, fresh food, shelter, and a living wage. Cox cites Georgios Kallis and other degrowth scholars who explicitly critique the Malthusian position of overpopulation, but he does not bring up these critiques in his own account.
Despite the above sentence, which enters into Cox’s analysis at the end of a long discussion about solidarity rationing, Cox is committed to reminding readers that the GND aims to stop carbon emissions in ways that will fundamentally uplift the most vulnerable. To do this, he maintains, the GND must be willing to deliberately scale back the economy and completely phase out fossil fuels by 2030, curtail the production and consumption of cars, air travel, and other fossil-fuel related activities, degrow the military and militarized law enforcement, end mass incarceration, and stop giving subsidies to industries that overproduce of civilian and military products. As Cox writes, we need a lower-energy economy with fewer goods, shorter working hours, and a motto of ‘sufficiency for all.’ Standardization and simplification will help ensure equitable distribution of essential resources and cut out the most wasteful parts of the economy.
The details of this kind of scaling back must be negotiated through local and participatory processes.
In thus countering the ‘eco-modernist’ approach of unhampered production in service of green luxury, Cox takes issue with those who do not see the need to deliberately scale back the economy. He argues instead that while many still believe that nuclear power or a battery-operated world will solve our problems, we must take a long, hard look at our ecological limits. If we are serious about meeting climate goals, for example, there can be no ‘high-speed rail’ as promised by Rep. Alexandra Ocasio-Cortez, because the concrete alone involved in such a project would contribute to an already-overshot cap of emissions. Rather, existing rail lines should be refurbished and extended in scaling back private transportation, while acknowledging that we need less—not more—energy use. The details of this kind of scaling back must be negotiated through local and participatory processes, but they would aim to include more public transportation, well-insulated and high-density housing, solar electric and water heating, and a new system of rationing not unlike that of the 1940s War Production Board. The good news is that the people responsible for the majority of emissions are in a relatively small class of consumers. The bad news is that we have to find a way to convince them to scale back the most.
In highlighting the above fact, Cox points out another common assumption: that simply taxing the 1% will be enough to stimulate the economy and re-build public infrastructure. Here the ambitious policies of both Sanders and Warren are called into question for not going far enough. Instead, Cox argues that the entire upper-middle class of the United States, which has a higher income than 96% of the world, will be adversely impacted by any ‘just transition’ that can equitably phase out fossil fuels. This is why Cox argues that a fair, effective climate policy will necessitate that ‘the 33% of American households with highest incomes will bear the greatest economic burden’ both in having to pay for economic restructuring, and in scaling back their own overblown consumption (109). The consumption of both its billionaire class and upper-middle class—the world’s 4%—must be heavily capped.
Restorative environmental justice
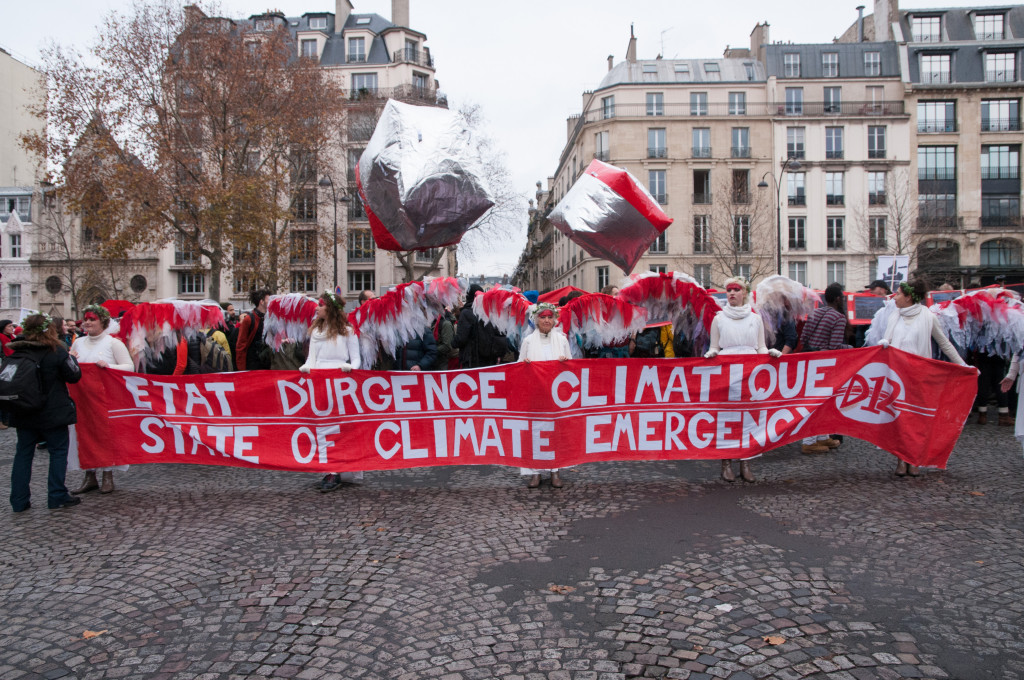
Instead of ‘leading the fight against climate change’ then, as the Green New Deal proposes, it would be more accurate to say that such legislation will begin to take some responsibility for centuries of uneven emissions, where the poorest parts of the world (who are responsible for only 15% of global emissions) feel the harshest and most brutal impacts of tropical storms, hurricanes, droughts, wildfires, and global migration. In fully recognizing the need for the U.S. to become accountable to these uneven causes and consequences, Cox acknowledges that there are many things which the Green New Deal gets right, or at least very close to right, in its vision of restorative environmental justice. Yet if the Green New Deal continues to rely upon the dream of a green energy economy to rival that of the fossil fuel industry, Cox warns, it will have to ignore this vision, as well as many of its own mandates to improve land use, preserve soil quality, and protect indigenous lands. Even if the U.S. refrains from further extractive practices on its own land, but continues mining precious metals across the world, it will still fail to enact this vision. Cox therefore suggests that the U.S. take part in a global fair-shares energy allocation that models the Green New Deal’s pro-worker and pro-poor economics, with the aim of globally ‘raising the floor and lowering the ceiling’ to put underdeveloped countries on par with developed ones.
Ultimately, Cox’s message is that, like the Southern Tenant Farmers Union, which pushed the New Deal to ensure both workers’ rights and racial justice, the climate movement must stand in solidarity with indigenous climate struggles against market solutions, even and especially those alluded to in the Green New Deal. The good news is that those who are not already a part of the 33% of upper-class consumers will have less to sacrifice, and will likely benefit from the GND’s demands for worker’s rights, universal healthcare, housing, jobs, and universal access to clean air, water, and food. As Cox reminds us, the 40% at the bottom of the economic pyramid have a net worth of negative $22,000, which is why we must, as he says, raise the floor and lower the ceiling. Yet those who turn their noses up to a ‘sufficiency for all’ planned economy—which include, as Cox points out, the ‘fully automated luxury’ green modernists of the Left—must also be brought face-to-face with the reality that we are already approaching, at best, a future of more limited consumption.
In writing this book, Stan Cox could not have anticipated that the spread of COVID-19 may itself present an emergency situation requiring the restructuring and planning of the economy. The recently passed CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act in the U.S., which includes loan forgiveness and emergency funds for economic relief, has attempted to intervene in this emergency for the sake of stabilizing the economy. Cox would likely respond that such drastic intervention must become the new normal, but not for the sake of the market. Rather, he would argue that such an emergency should be an impetus for simplifying, standardizing, and restructuring production and consumption. Cox argues that this is not idealism, but necessity. By 2030 or 2040, if our aims and policies turn out to have been insufficient, as he points out, it will have been too late.
Natalie Suzelis is a Ph.D. candidate in Literary and Cultural Studies at Carnegie Mellon University. Her research analyzes the environmental and cultural history of capitalist development in early modern literature.